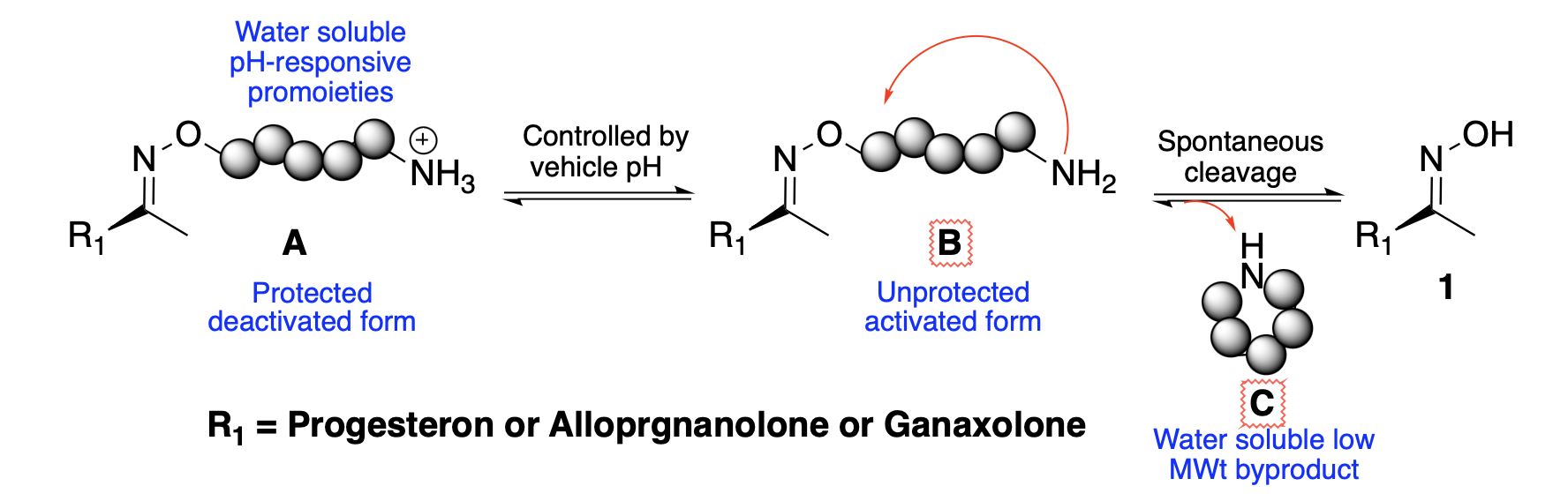
Neurosteroids are a class of endogenous steroids synthesized within the central nervous system to modulate neuronal activity and function. Neurosteroids play critical roles in cognition, mood regulation, stress response, and neuroprotection, influencing synaptic transmission and neurotransmitter release to impact brain function and behavior profoundly. Progesterone, allopregnanolone, and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) have shown promise in preclinical studies for their neuroprotective effects in conditions such as traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases. Recent advancements in clinical development have led to FDA approvals for brexanolone (Zulresso) and ganaxolone (Ztalmy®), marking significant milestones in neurosteroid-based therapy. However, challenges such as poor solubility and complex pharmacokinetics hinder their efficacy. Our ongoing research focuses on synthesizing C20-oxime-based prodrugs for neurosteroids to enhance solubility and bioavailability while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. We aim to overcome these limitations through pH-sensitive self-immolation prodrug linkers (Figure 1), enabling the effective delivery of neurosteroids for improved neurological and psychiatric outcomes.
Figure 1. pH-responsive prodrug strategy